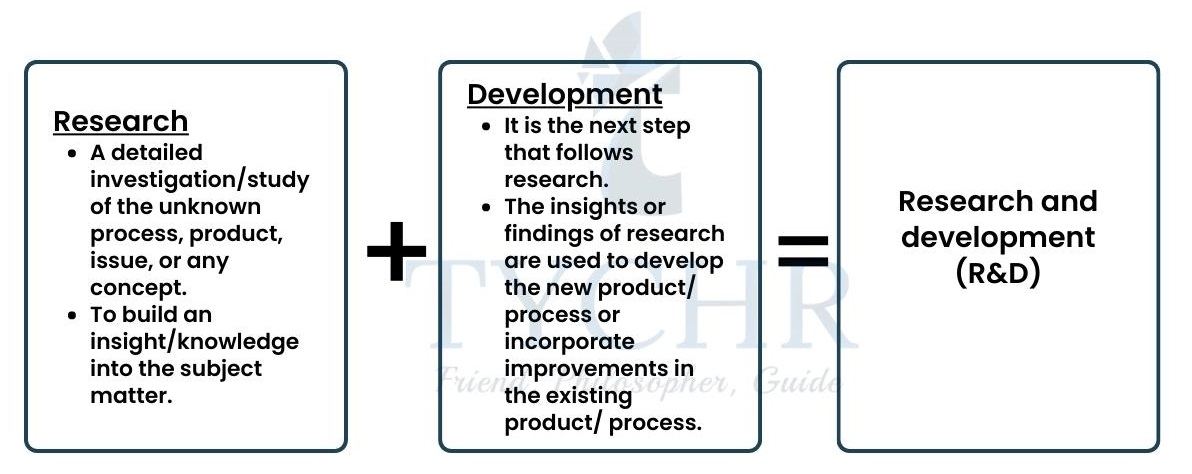
research and development and innovation Notes
Research and development and Innovation
Importance of Research and development to businesses:

- Provides competitive advantage to business- E.g.- Daikin is a globally recognized air-conditioner brand, which has rooted its position across the globe because of the constant market research and developments in technology and processes.
- Business wins customer loyalty- Dell has a large customer base and stands as India’s most trusted brand in laptops. Dell has consistently focused on the necessary research and technological developments. With the exclusive features at reasonable prices, Dell has always kept its customers satisfied.
- High prices can be charged for the products- A detailed market research lets the business organization to improve its existing process/ product or launch a new product that can easily attract the customers of the target market. This gives the organization an advantage to charge higher prices.
- Publicity- Facebook, a global social networking service provider has gained immense publicity due to its user- friendly features and continuous technological developments.
Limitations of Research and development to businesses:
- Expensive affair- Excessive financial and human resources are required to carry out R&D. The cost of the companies which make huge investments in research and development hikes up significantly. Microsoft had spent close to 8164 billion dollars in 2008-09 on research and development.
- High failure rate- Even a careful and detailed research and development might be a failure. Most of the time, the ideas are not materialized, or new products are not launched due to non-feasibility of the idea.
- Budgetary constraint- R&D demands heavy investment and this fact often leads to funding problems because all the enterprises have a defined budget for expenditure.
What is innovation?
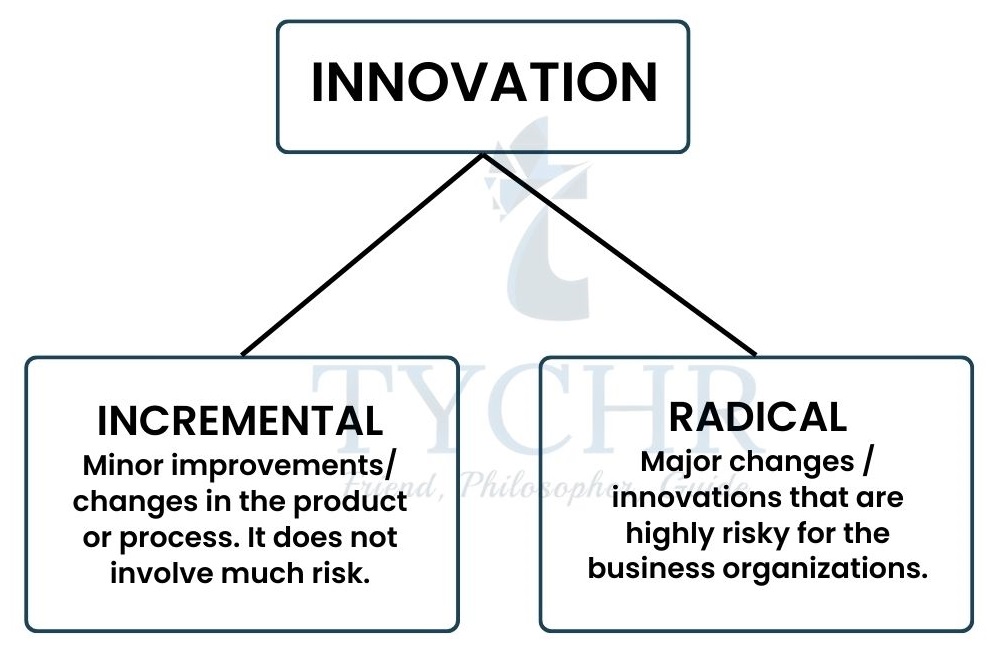
- Innovation results from R&D
- It is a process of continuous improvement in the existing product/ process or launching of new products, with the use of new ideas and creativity.
- Innovation improves the marketability of the product/ service.
- Innovation can be done only after understanding the needs of customers.
- Innovation gives a competitive edge to the business organization.
Well-known examples of innovations used by business organizations:

- LG recently launched the flexible OLED TV in the 65-inch screen, whereby the TV screen rolls down to fit in a box once done watching. This innovation by the multinational electronics company is remarkable.
- Amazon, the world’s leading e-commerce company, has launched Amazon Prime service, which is again a significant innovation that heavily increased Amazon’s market share.
Types of innovation
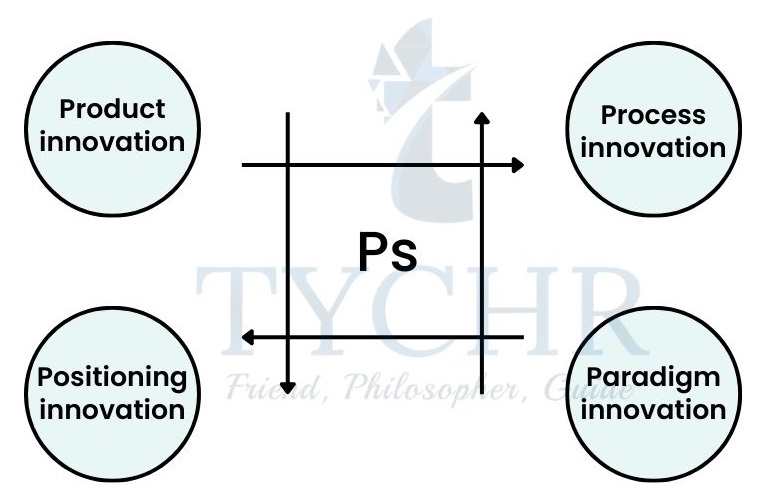
1. Product innovation
- New product launch
- Development in existing products to improve marketability and profitability.
- Amazon Kindle is an example of product innovation from Amazon, the world’s leading e-commerce company.
2. Process innovation
- Positive changes/ improvements in the methods of carrying out business operations.
- It includes use of new technologies to improve the processes.
- E.g.- Most of the firms are using automated digital techniques to improve productivity and consumer satisfaction.
3. Positioning innovation
- The context of the product is changed.
- The product is re-positioned with the changed background/ story in the minds of customers.
4. Paradigm innovation
- A radical change that changes the nature of a certain market.
- Innovation by a business organization affects the functioning of other businesses in the industry.
INNOVATION | CREATIVITY | INVENTION |
Incorporation of changes/ improvements in the product/ process. It happens after a valuable research and development. It is an ongoing process that comprises new inventions each time. | On the other hand, creativity is a vital prerequisite to innovation. Without creative minds, innovation is not possible. Creativity can be clearly defined as the ability of an individual or organization to generate new and unique ideas that can further be used to bring innovation. | Invention is the application of creative ideas to develop new products/ processes. Invention is a vital process in a business organization. |
E.g.: Recently, Ola came up with the motorbike services and thus broadened the existing range of its services. | E.g.: Ola Cabs, the leading mobility services platform started with the creative idea of connecting the customers with the cab services online. | E.g.: With the creative ideas of the founders of Ola, the platform was invented in 2010. |
- E.g.: Reliance is an apt example to understand the meaning of paradigm innovation. Reliance, a giant telecommunications brand had launched Reliance Jio in 2015 which came up with the offer of unlimited calls and data at a minimum price. This innovative step by Mr. Mukesh Ambani led other operators like Vodafone, Airtel to change their price and offer structure as well.
Factors affecting innovation:
1. Nature of the industry in which the business is thriving
2. Competitors’ spending plans in R&D
3. Risk profile of the business
4. Government policies
5. Finance/ budget of the firm
Difference between innovation, creativity, and invention
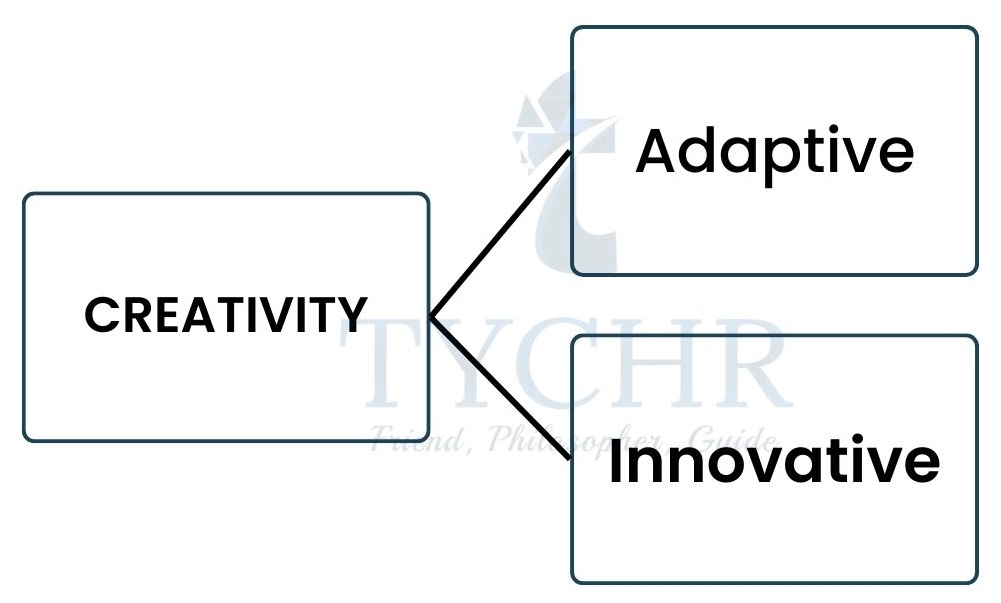
- Adaptive creativity
A silent and a less risky category of creativity whereby the idea is generated to adapt with the embedded paradigm in the industry or the organizational policies and culture. - Innovative creativity
An aggressive form of creativity which involves huge risk since completely new ideas are generated for the development of new products/ processes or improvement in the existing product/process.
Research and development and the CUEGIS concept
CUEGIS (Change, culture, ethics, globalization, innovation, strategy) factors play an important role in affecting the research and development decisions of the business organization. Before considering the R&D strategies, the ethical impacts of the development and culture of the organization need to be considered before framing any strategy. In today’s ever-increasing competitive scenario, it has become vital for an organization to invest in the research and development to promote innovation. In modern days, the government is constantly trying to encourage the firms to undertake R&D through the protection of IPR (Intellectual Property Rights).
- Intellectual property rights- Legal rights to exclusive ownership of intangible property which includes the creation, idea, know-how or invention that belongs to the owner.
- Patent- Right that is granted by the United States Patent and Trademark Office to the owner of original invention for a certain duration, to protect the asset from being used by any competitor. This right provides incentive to the innovators to continue developing innovative products/ services without any fear.
- Trademark- A trademark is a word, phrase (slogan) or design(logo) that distinguishes one brand from the other. Trademarks do not expire after a certain period. They last forever till the organization exists.
- Copyright- A copyright is a sort of protection received by the creators of original works such as music, art, poetry, movies, books, songs, computer software, etc.

