IB Physics SL Paper 1 Question Bank
The IB Physics SL Paper 1 question bank is a great resource for students preparing for the IB Physics SL exam. The question bank includes a wide range of questions, from multiple choice to essay questions, that covers all of the topics on the IB Physics SL syllabus. This makes it an invaluable resource for students who want to make sure they are prepared for every possible question on the exam.
Time: 45 minutes
Instructions to candidates
- Answer all the questions.
- For each question, choose the answer you consider to be the best and indicate your choice on the answer sheet provided.
- A clean copy of the physics data booklet is required for this paper.
- The maximum mark for this examination paper is [30 marks].
1.) What is a unit of force?
A.) m/Js
B.) J m
C.) J/m
D.) J/ms
Answer: C
Explanation:
The metric unit of force is the joule per meter (J/m). In the field of mechanics, a joule is defined as the amount of work required to move an item one meter across a distance of one newton in the direction of application (1 J = 1 Nm). Newton is therefore equal to one joule per meter.
2.) The length of the side of a cube is 3.0 cm ± 5%. The mass of the cube is 27.0 g ± 7%. What is the percentage uncertainty of the density of the cube?
A.) 22
B.) 12
C.) 8
D.) 14
Answer: A
Explanation:
Volume of the cube is 3 x 3 x 3, therefore the uncertainties will also get added 3 times (not multiplied). Therefore 5 x 3 = ± 15% Even though density = mass / volume, the percentage uncertainties get added, therefore, the percentage for the density is 15 + 7 = ± 22%
3.) A truck has an initial speed of 25 ms-1. It decelerates at 5.0 ms-2. What is the distance taken by the truck to stop?
A.) 12.5 m
B.) 5 m
C.) 125 m
D.) 62.5 m
Answer: D
Explanation:
To find the distance, the time needs to be calculated. Therefore, using an equation of motion, v = u + at and substituting the values that we have, we have
0 = 25 + (-5)t
v is the final speed which is 0 since the question says that the truck comes to a stop. The deceleration is 5 so the value of the acceleration would be -5. Therefore, calculating t, we have 5t = 20 → t = 4 s.
Using the time, the distance can be found using another equation of motion: s = ut + ½ at2 where s is the distance. Therefore, substituting the values that we have,
s = (25)(5) + ½ (-5)(5)2
S = 125 + (-62.5) = 62.5 m
4.) A heat engine does 250 J of work during one cycle. In this cycle, 750 J of energy is wasted. What is the efficiency of the engine in percentage?
A.) 25%
B.) 33.3%
C.) 50%
D.) 75%
Answer: A
Explanation:
Total energy is 250 + 750 = 1000 J
Efficiency of the engine = (Work done/Total energy)*100
= (250/1000)*100 = 25%
5.) A driving force F acts on a car which moves with a constant velocity v. The quantity Fv is equivalent to:
A.) Useful power released by the engine of the car
B.) Work done by the car
C.) Energy produced by the car
D.) Rate of change of momentum of the car
Answer: A
Explanation:
The quantity Fv is a result of multiplying the driving force and the velocity (Force x Velocity). The output you get by multiplying these quantities is Power. Power = Force x Velocity
6.) There is water boiling in a pot. The boiling water molecules leave to form vapor. The temperature of the water and the vapor are the same. How do the average kinetic and potential energy of the molecules change when the liquid water boils to form vapor?
A.) No change in average potential energy & no change in average kinetic energy
B.) No change in average potential energy & increase in average kinetic energy
C.) Increase in average potential energy & no change in average kinetic energy
D.) Increase in average potential energy & increase in average kinetic energy
Answer: C
Explanation:
When there is a phase change, the temperature stays constant therefore implying that the average kinetic energy also remains unchanged. During the vaporization stage, there is a certain amount of energy that the molecule attains thereby increasing the internal energy of said molecules. This means that the average potential energy increases.
7.) A sound wave travels from hot air to cold air. How does the frequency and the wavelength of the wave change?
A.) Frequency remains unchanged & wavelength increases
B.) Frequency remains unchanged & wavelength decreases
C.) Frequency increases & wavelength increases
D.) Frequency decreases & wavelength decreases
Answer: B
Explanation:
Wave velocity = frequency x wavelength
Therefore, when the temperature decreases, velocity decreases thereby decreasing the wavelength of the wave. The frequency of the wave is not affected by the temperature of the air so it remains unchanged.
8.) A mass is moving along a horizontal circle with constant speed. Which of the following options are correct about the magnitude and direction of the mass?
A.) Magnitude is constant and direction is constant
B.) Magnitude is constant and direction is changing
C.) Magnitude is changing and direction is constant
D.) Magnitude is changing and direction is changing
Answer: B
Explanation:
Since the speed is a scalar quantity and only represents the magnitude, the magnitude will remain constant as the mass moves along the horizontal circle. However, the velocity changes since there is a change in the direction at every point when the circle moves across the horizontal circle.
9.) The average binding energy per nucleon for Carbon 12 is 7.68 MeV. What is the total energy required to separate the nucleons of one nucleus of Carbon 12?
A.) 92 MeV
B.) 46 MeV
C.) 138 MeV
D.) 174 MeV
Answer: A
Explanation:
Binding energy per nucleon = Binding energy (B) / Number of nucleons (A)
Since we need to find the binding energy, the equation can be rearranged
Binding energy (B) = Binding energy per nucleon x Number of nucleons
Number of nucleons is 12 and binding energy per nucleon is 7.68, so:
Binding energy (B) = 12 x 7.68 = 92.16 MeV approximately, 92 MeV
10.) A horizontal string has one end fixed to a wall. As seen, a transverse pulse travels along the string.
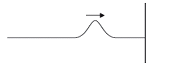
Which of the following claims about the reflected pulse in relation to the forward pulse is true?
I) The pulse is inverted
II) It has less energy
III) The pulse moves more slowly
A.) I and II
B.) I and III
C.) I, II and III
D.) II and III
Answer: D
Explanation:
When the wave hits the wall, some of the energy is transferred to the wall. Therefore, after some of the energy passes on and when the wave is reflected, the pulse is reflected with lesser energy. Furthermore, when the pulse has lesser energy, it is also bound to move with a lower velocity due to its lesser energy.
11.) A proton is moving with a velocity v in a magnetic field B. What is the direction of the magnetic force acting on the proton?
A.) Parallel to v
B.) Perpendicular to v and B
C.) Perpendicular to v
D.) Perpendicular to B
Answer: C
The direction of the magnetic force acting on a charged particle moving in a magnetic field is given by the right-hand rule. The force is perpendicular to both the velocity of the particle and the magnetic field.
12.) An object moves in a circular path with a constant speed. What is the direction of its acceleration?
A.) Towards the center of the circle
B.) Tangential to the circle
C.) Perpendicular to the circle
D.) Away from the center of the circle
Answer: A
A concave mirror can form either a real or a virtual image depending on the position of the object relative to the focal point of the mirror.
13.) A wave with a frequency of 1000 Hz has a wavelength of 0.1 m. What is the speed of the wave?
A.) 10 m/s
B.) 100 m/s
C.) 1000 m/s
D.) 10,000 m/s
Answer: B
The speed of a wave is equal to the product of its frequency and wavelength. Therefore, v = fλ = 1000 Hz x 0.1 m = 100 m/s.
14.) Which of the following statements is true about the photoelectric effect?
A.) The energy of the ejected electrons depends on the intensity of the incident light
B.) The energy of the ejected electrons depends on the frequency of the incident light
C.) The number of ejected electrons depends on the intensity of the incident light
D.) The number of ejected electrons depends on the wavelength of the incident light.
Answer: B
The photoelectric effect is the emission of electrons from a metal surface when light of a certain frequency is incident on it. The energy of the ejected electrons depends on the frequency of the incident light, not its intensity. The number of ejected electrons depends on the intensity of the incident light, not its wavelength.
15.) A circuit contains a resistor, a capacitor, and an inductor in series. What is the phase difference between the current and the voltage across the capacitor?
A.) 0 degrees
B.) 45 degrees
C.) 90 degrees
D.) 180 degrees
Answer: C
In a series circuit containing a resistor, capacitor, and inductor, the voltage across the capacitor lags the current by 90 degrees. The voltage across the resistor and the inductor also have a phase difference with the current, but it is different from that of the capacitor.
16.) Which of the following statements is true about the behavior of waves at a boundary between two media?
A.) The frequency of the wave changes at the boundary
B.) The amplitude of the wave changes at the boundary
C.) The wavelength of the wave changes at the boundary
D.) The speed of the wave changes at the boundary
Answer: D
When a wave passes from one medium to another, its speed changes because the properties of the medium affect the wave’s propagation. The frequency, amplitude, and wavelength of the wave remain the same.
17.) A ball is thrown straight up into the air. At the highest point of its trajectory, which of the following statements is true?
A.) Its velocity is zero and its acceleration is zero
B.) Its velocity is zero and its acceleration is not zero
C.) Its velocity is not zero and its acceleration is zero
D.) Its velocity is not zero and its acceleration is not zero
Answer: A
At the highest point of its trajectory, the ball has zero velocity because it has reached its maximum height and is about to change direction and begin falling back down. However, its acceleration is not zero because the force of gravity is still acting on it, causing it to decelerate as it rises and then accelerate as it falls.
18.) A person is standing on a bathroom scale inside an elevator that is accelerating upwards. How does the reading on the scale compare to the person’s actual weight?
A.) The reading is greater than the person’s weight
B.) The reading is equal to the person’s weight
C.) The reading is less than the person’s weight
D.) It depends on the speed of the elevator.
Answer: A
When the elevator is accelerating upwards, the normal force exerted by the scale on the person is greater than the person’s weight. This is because the net force on the person is the sum of the normal force and the person’s weight, and the net force must equal the mass of the person times their acceleration, which is greater than g. As a result, the scale reading will be greater than the person’s weight.
19.) Which of the following is an example of elastic collision?
A.) A golf ball hitting the ground and coming to a stop
B.) A ball bearing colliding with a spring and compressing it
C.) Two cars colliding and sticking together
D.) A tennis ball bouncing off a wall and returning to the player
Answer: D
In an elastic collision, both the momentum and the kinetic energy of the system are conserved. When a tennis ball bounces off a wall, it experiences an elastic collision and returns to the player with the same speed it had before the collision. A golf ball hitting the ground, a ball bearing colliding with a spring and compressing it, and two cars colliding and sticking together are all examples of inelastic collisions, where the kinetic energy is not conserved.
20.) Which of the following is not a characteristic of a simple harmonic oscillator?
A.) The oscillation frequency is constant
B.) The maximum displacement from equilibrium is proportional to the amplitude
C.) The motion is periodic
D.) The restoring force is proportional to the displacement
Answer: B
In a simple harmonic oscillator, the motion is periodic, the oscillation frequency is constant, and the restoring force is proportional to the displacement from equilibrium. However, the maximum displacement from equilibrium is not necessarily proportional to the amplitude of the oscillation, since the amplitude can be changed by external forces acting on the oscillator.
21.) Which of the following is true about the image formed by a concave mirror when the object is located beyond the focal point?
A.) The image is virtual, upright, and magnified
B.) The image is real, inverted, and magnified
C.) The image is virtual, inverted, and diminished
D.) The image is real, inverted, and diminished
Answer: D
When the object is located beyond the focal point of a concave mirror, the image formed is real, inverted, and diminished. The distance of the object from the mirror is greater than the focal length, so the image is formed between the focal point and the center of curvature of the mirror. The size of the image is smaller than the size of the object, and the image is inverted.
22.) A student measures the time taken for a pendulum to complete one oscillation as 2.45 seconds. What is the uncertainty in this measurement if the uncertainty in the stopwatch is ±0.01 seconds?
A.) ±0.001 s
B.) ±0.010 s
C.) ±0.100 s
D.) ±0.245 s
Answer: B
The uncertainty in the measurement is equal to the uncertainty of the stopwatch, which is ±0.01 seconds.
23.) Two identical samples of a gas at different temperatures are mixed. What will happen to the entropy of the system?
A.) Entropy will increase
B.) Entropy will decrease
C.) Entropy will remain constant
D.) Not enough information to determine
Answer: A
According to the second law of thermodynamics, entropy of a closed system will always increase or remain constant.
24.) A sound wave is emitted from a speaker and travels through air to a listener. If the distance between the speaker and the listener is doubled, what happens to the intensity of the sound wave at the listener’s location?
A.) The intensity is halved
B.) The intensity is doubled
C.) The intensity is quadrupled
D.) The intensity remains the same
Answer: A
The intensity of a sound wave is proportional to the square of the amplitude of the wave and inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the source. If the distance between the source and the listener is doubled, the intensity of the sound wave at the listener’s location is reduced by a factor of four, since the sound wave has spread out over a larger area.
25.) A negatively charged rod is brought near a neutral conductor. What happens to the electrons in the conductor?
A.) The electrons move away from the rod
B.) The electrons move towards the rod
C.) The electrons move to the other end of the conductor
D.) The electrons do not move
Answer: B
A negatively charged rod will repel the electrons in a neutral conductor, causing them to move towards the side of the conductor closest to the rod.
26.) What is the relationship between the entropy change of a system and its surroundings in a reversible process?
A.) They are equal
B.) They are opposite in sign
C.) They are both positive
D.) They are both negative
Answer: A
In a reversible process, the entropy change of the system and surroundings are equal and opposite in sign, meaning their sum is zero.
27.) A gas undergoes an isothermal process. What happens to the internal energy of the gas?
A.) It increases
B.) It decreases
C.) It remains constant
D.) It cannot be determined without additional information
Answer: C
In an isothermal process, the temperature of the gas remains constant, which means the internal energy of the gas also remains constant.
28.) Which of the following is an example of an endothermic process?
A.) The combustion of gasoline in a car engine
B.) The dissolution of sugar in water
C.) The melting of ice
D.) The condensation of water vapor
Answer: C
In an endothermic process, heat is absorbed by the system from the surroundings. The melting of ice requires heat to be absorbed by the ice, making it an endothermic process.
29. A student is measuring the length of a metal rod using a ruler with markings every 1 mm. The ruler is not perfectly aligned with the rod, so the student estimates the length to be 24.3 mm. What is the absolute uncertainty of the measurement?
A.) 0.05 mm
B.) 0.1 mm
C.) 0.2 mm
D.) 0.5 mm
Answer: B
The absolute uncertainty is half of the smallest division of the ruler, which is 0.1 mm.
30.) A power plant generates electricity by burning coal. The heat produced by burning the coal is used to boil water, which then drives a turbine. What type of energy transformation occurs in this process?
A.) Chemical energy to electrical energy
B.) Electrical energy to mechanical energy
C.) Mechanical energy to thermal energy
D.) Thermal energy to mechanical energy
Answer: D
The heat produced by burning the coal is thermal energy, which is converted to mechanical energy by the turbine.


