maketing planning Notes
Marketing plan
A marketing plan is a document or a report that outlines the marketing strategies to be used to achieve the marketing objectives of the organization.

- SMART (Specific, Measurable, Agreeable, Realistic and Time-constrained) marketing objectives.
- Market research methods that are to be used to identify the target markets.
- Analysis of the strengths and weaknesses of the competitors.
- Marketing mix (product, price, place and promotion) strategies.
- Marketing budget details
- Anticipated problems and issues and the solution/ strategies to deal with them.
Now, how would you define marketing planning?
The systematic process of preparing the marketing plan is called marketing planning.
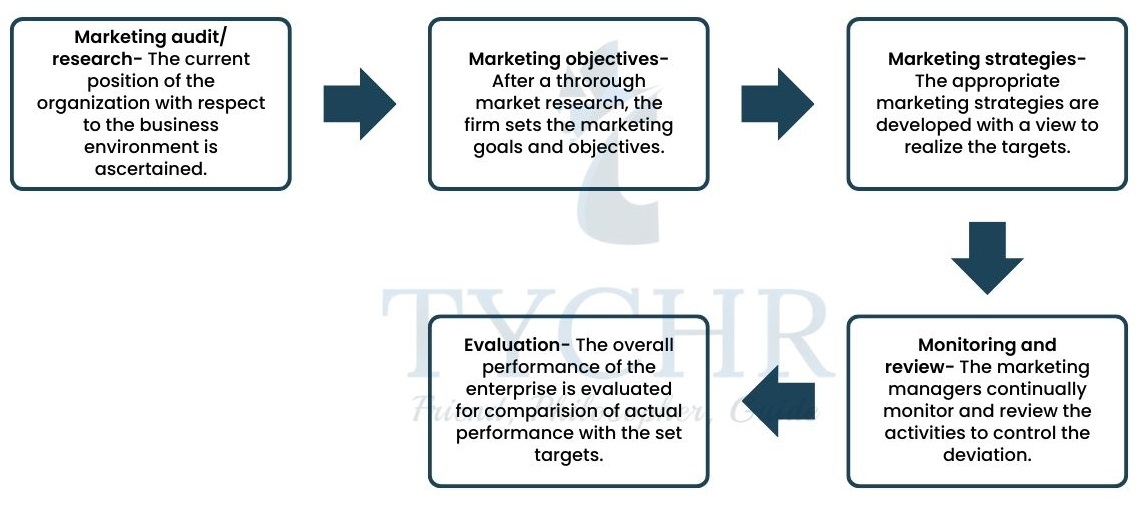
Advantages of marketing planning | Limitations of marketing planning |
|
|
Marketing mix
Marketing mix is the combination of the marketing strategies pertaining to the seven key elements. An integrated marketing mix (important for the success of the organization) implies that the marketing decisions associated with the Ps must complement each other to bring out a clear and consistent message about the product for the customers.
Key elements of the marketing mix:
Four important Ps = Price, product, place and promotion. Other 3Ps = People, process and physical evidence
The 7Ps have been explained in detail in the chapter ‘The four Ps’ and ‘The extended marketing mix’.
Target markets and the market segmentation

A market segment refers to the group of customers (part of the whole market) with similar characteristics/ requirements.
Market segmentation is the process of differentiating the whole market into small segments or groups that consist of the customer with similar needs, preferences and characteristics. It is also called differentiated marketing.
The business organizations segment their market on the basis of customer profiles (demographic, psychographic and geographic characteristics of consumers in different markets).
Why do businesses segment their markets?
- For understanding the customers better- Market segmentation helps the business organization to understand the needs and wants of its customers in a better manner.
- To identify growth opportunities- Effective segmentation helps the business to identify growth opportunities, if any.
- Market segmentation helps the business to identify the target markets and set the marketing objectives and
prepare the marketing strategies accordingly.
Criteria for successful market segmentation:
- The market segments must be differentiated from each other on the basis of customer profiles.
- Businesses must be actionable and must provide suitable products to the customers of each market segment subject to their needs and wants.
- The size of each market segment and the purchasing power of consumers in the segment must be measurable.
- The businesses must ensure that the suitable products are accessible to the customers of each market segment on time and in a cost-effective manner.
Each market segment must be large enough to be able to generate a substantial amount of profits.
Some of the creative demographic segmentation acronyms used by marketers:
DINKY – Double income, no kids yet.
OINK – one income, no kids.
GLAM – graying, leisured, affluent, middle-aged
SITCOM – Single income, two children, outrageous mortgage.
Advantages of market segmentation | Limitations of market segmentation |
● Market segmentation helps the businesses to identify their target markets and thus design the products accordingly to increase the sales. | ● Market segmentation increases the R&D, production and promotional costs of selling different products with different marketing strategies to different market segments/ target markets. |
● Market segmentation eliminates the need to focus on the whole market to sell their products. Marketing strategies can be specifically devised for the particular target market and money wastage can thus be avoided. | ● Businesses solely focus on the target markets to sell their products. Specialization creates the possibility of loss or failure if the consumers in those market segments suddenly change their preferences/habits. |
Positioning
Positioning is the process that is used by the marketers to establish their product or brand in the minds of target customers at a distinctive position to receive competitive advantage. The technique used by them to position their product is called market mapping whereby a product or perception map is created to understand the customer perceptions of the product or brand in relation to others in the market.
Three stages to positioning
- Competitive advantages of the product are identified.
- Marketers decide on which aspects of the above strengths, the product is to be marketed.
- Appropriate marketing strategy is developed for each market segment to position the product/brand.
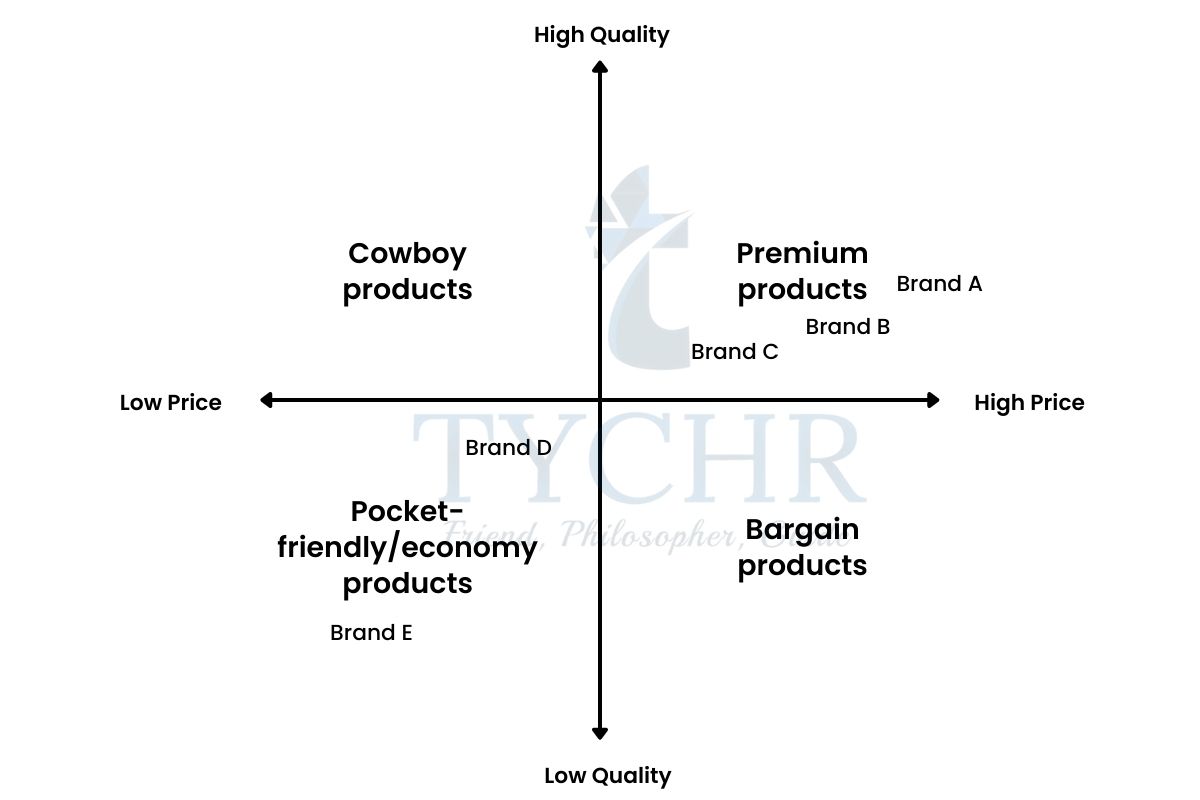
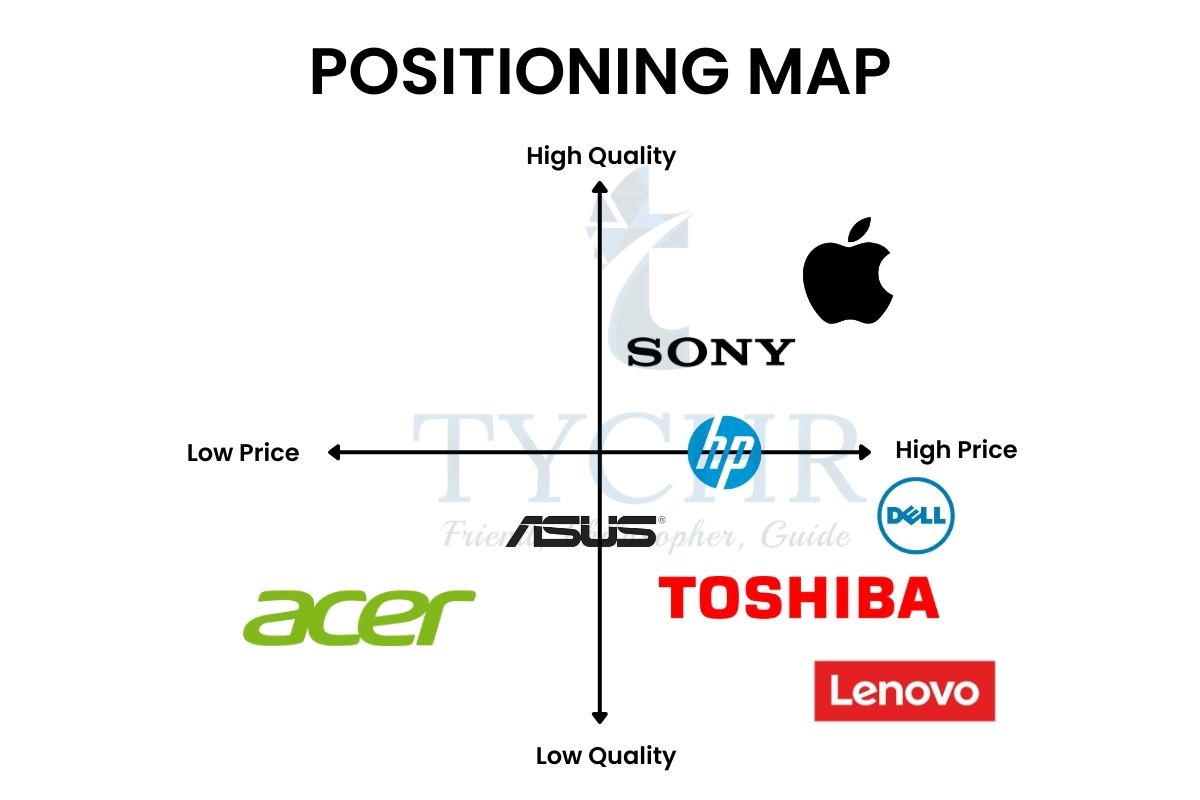
Product position or perception map
- The term position/perception map was coined by Jack Trout (he was the owner of consulting firm, Trout and Partners) in 1969.
- The two variables price and quality are used to develop the grid. The positioning map is simple and easy to interpret the customer perceptions of a particular product or brand.
- The businesses can identify the potential gaps in the market through the study of the position map. This opens the business to new opportunities that an be capitalized to build overall corporate image.
- Premium products- High quality and high-priced products.
- Cowboy products- Low quality but highly priced products.
- Bargain products- These products are of high quality sold at low prices to boost sales.
- Economy products- Low quality but low-priced as well for price-sensitive customers
Unique-selling point
Unique selling point or proposition is the differentiating aspect of a business, brand or product which makes that product or brand unique and gives it a competitive advantage.
A USP is difficult to find but it allows the business to differentiate its products from the rivals/competitors and build its corporate image.
For instance, the USP of Amazon, the world’s leading ecommerce company is its excellent customer service.
Differentiation
The act of distinguishing a business or its products from its rivals or competitors in the industry is called as differentiation. The aim of differentiating the brand or product is to establish it as a unique product or brand in the minds of target customers.
Methods of differentiation
- Product- This differentiation can be done in terms of quality, design, features or composition of the product.
- Price- Prices can be kept low, discounts can be offered or any other suitable pricing strategy can be used.
- Place- The businesses use various channels of distribution to make their products reach the customers.
- Promotion- The business organizations can also differentiate their business or products on the basis of promotion strategies that are used to position the products.
- Physical environment- Physical environment and location can be a vital differentiator for many businesses such as hotels and restaurants, schools, etc. These organizations can use the apt location and environment for the competitive benefits.
- People- The human resources (workforce) of the organization who are responsible for implementing the marketing strategies can be motivated with the provision of better incentives and can be trained well to compete with the rival firms.
- Process- Any activity in the organization is carried out in the form of a well-defined process. The stages in the process or the materials or the strategies used to complete the process can be altered to improve the efficiency of that activity. For instance, the use of automated machines and equipment in the production process can improve the production efficiency.
- Packaging- Lux, Vaseline, Dove, etc. are some top brands of body lotions and creams that are used worldwide by the customers. The above brands are differentiated from each other in terms of their color, quality and materials of packaging.
Marketing planning and the CUEGIS concepts
The marketing managers of the business organization prepare a detailed plan that lists down the strategies and methods of marketing and the solutions of problems in advance. But the marketing plan is likely subject to constant evolution because of the CUEGIS (change, culture, ethics, globalization, innovation and strategy) factors in play. The changes in organizational structure, organizational culture, ethics, etc. is inevitable because of the frequent changes in the business environment. Hence, the marketing managers keep on revising and updating the plans subject to the changes that are anticipated.

