sources of finance Notes
What do we interpret from the term ‘finance’?
In simple words, Finance is the management of money pertaining to organizations, companies, or government. It includes all the activities such as investing, borrowing, lending, savings, etc.

Finance spent on acquiring and the maintenance fixed assets. Fixed assets include Land, buildings, machinery, equipment, etc. that are not meant for resale but for the purpose of generation of revenue in the business.
Payments made to meet the regular/daily operational costs of a
business. Example- Wages, Rent, Salary, etc.
Classification of the sources of finance:
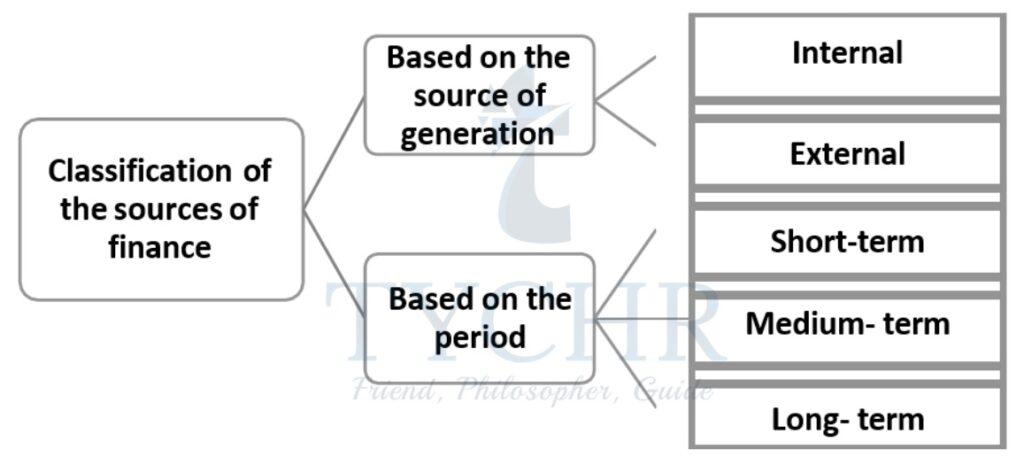
INTERNAL SOURCES OF FINANCE
Finance/ Capital generated internally by the business which does not put any liability on the business’s head. There is no direct cost except for the opportunity cost.
PERSONAL FUNDS | RETAINED PROFITS | SALE OF ASSETS |
Funds employed by the owners at their personal level, from their savings. | The profits that are left after the payment of dividends (shareholders) and taxes (government). These are generally used for expansion and other future activities related to the growth of business. | Sometimes, businesses raise money from the sale of dormant assets, the assets that are no longer useful such as old machinery/ equipment. |
EXTERNAL SOURCES OF FINANCE
SHARE CAPITAL
- Primary source of finance for limited liability companies.
- The small certificates called shares are issued to people to raise capital money. In return, the shareholders receive dividends (share of profits of the company).
- Private limited companies cannot sell these shares to public (saleable only to close relatives and
family members). - Public limited companies can get their shares issued on the stock exchange.
LOAN CAPITAL
- Capital money borrowed from a lending institution/ individual at a nominal interest (coupon)
- There are several ways in which an organization can borrow money-
- From the commercial lending institutions known by the name of banks.
- From the debenture holders by issuing the certificates called as debentures. The coupon (interest) is paid to these debenture holders periodically. Unlike shareholders, debenture holders do not possess the voting rights in the company.
- Loans are also provided by other financial institutions such as NBFCs (Non- Banking Financial Institutions), Insurance and mortgage companies.
- Small businesses generally borrow business development loans to cater to specific development needs of the business.
OVERDRAFTS
- A short- term source of finance that is provided by the bank to its account holders.
- The bank allows the account holder to withdraw money in excess of the funds in the account.
- The interest rate is quite high on overdraft as the interest is charged on a daily basis.
- This option of finance is chosen by businesses to deal with minor cash flow problems.
TRADE CREDIT
- Vital source of finance for sole proprietorships and partnerships.
- Trade credit is another short- term source of finance whereby the one business organization (supplier- creditor) allows the other business organization (debtor) to buy now and pay later by means of trade credit.
- The credit period varies between 30-60 days.
- Credit card is the commonly used credit instrument provided by banks and other financial institutions (creditors). There is a set credit limit for the customers. These cards are generally chargeable, and interest is charged as penalty if the amount is not paid within the due date.
GRANTS AND SUBSIDIES
- Grants are the one-off payments (financial gifts) provided by the government to the eligible businesses to promote their growth and expansion. These are non- repayable funds. Grants are mostly provided to start-ups to help them overcome financial problems in the beginning.
- Unlike grants, Subsidies are the one-off payments provided by the government to business organizations for the benefit of society. The subsidy is provided with a view to make the basic goods and services affordable for marginal income families. These enterprises charge a minimum price for the products and make profits out of the financial support extended by the government.
DEBT FACTORING
- Debt factoring is an immediate source of finance where some debt factoring institutions provide 80-85% of the amount owed by the debtors of the organization, within 24 hours once the application is approved.
- This is beneficial for businesses which suffer from cash flow problems. These institutions charge high fees for this service and take the responsibility to chase debtors for money.
HIRE-PURCHASE AND LEASING
Leasing
- In leasing, there is a contract between two parties- the lessor (the leasing company) and the lessee (customer)
- This is a feasible source of finance for the businesses which suffer from lack of finance and cannot buy the assets. This is a good source of finance only in the short-term.
- The assets such as machinery, equipment, furniture, etc. are leased by the owner (lessor) to the customer for rent.
- The rent paid acts as an expense and thus the business is able to save on taxes.
- Sale-and-leaseback is a different leasing concept that acts as a source of finance for businesses. The owner of the assets sells them to raise finance and leases them back. Ownership is transferred but the assets are not transferred.
Hire- purchase
- Hire purchase is different from leasing. The assets are transferred by the creditor to the business organization on the installment basis.
- The ownership of the asset gets transferred to the hiring business once the last installment is paid. A small amount of security deposit is paid by the hirer to use the assets.
VENTURE CAPITALISTS AND BUSINESS ANGELS
- Venture Capital is a form of private equity capital whereby the group of professional investors provide financial help to the startups and small businesses which have growth potential, in return of equity stake.
- On the other hand, Business angels are wealthy individuals who invest their personal funds in a startup or small business that has the potential to grow in the long term.
- Venture capitalists can invest a comparatively higher amount than the business angels.
Few factors that influence the choice of source of finance:
- The total amount of funds required.
- The opportunity cost of raising the funds through internal or external sources.
- The size of existing debts and borrowings that the business is liable to pay to its lenders.
- Duration and purpose for which the finance is required.
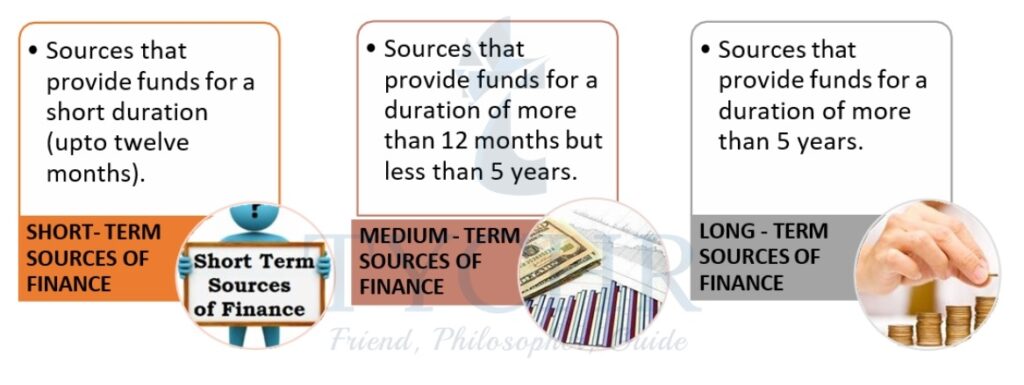
Find the table drawn below for the better comprehension of the internal and external sources of finance by the timeframe and the type of organization.
Sources of finance | Short term | Medium term | Long term | Private limited company | Public limited company | Sole proprietorships and partnerships | NGOs |
Internal | |||||||
| Personal funds | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Retained earnings | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ||
| Sale of assets | ✔ | ✔ | |||||
External | |||||||
| Share capital | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Loan capital | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Overdrafts | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Trade credit | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Grants and subsidies | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |
| Venture capital | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ||
| Business angels | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |||
| Debt factoring | ✔ | ✔ | |||||
| Leasing | ✔ |
Sources of finance and the CUEGIS factors:
The factors that influence the choice of source of finance in a business organization have been mentioned above. Those are the theoretical factors that influence the choice of source of finance. In practice, the CUEGIS (change, culture, ethics, globalization, innovation, and strategy) factors too have to be considered by the management before arriving at a final decision pertaining to the choice of feasible source of finance.

