IB Biology SL Paper 1 Question Bank
Check Out Our Results

OXFORD UNIVERSITY
(QS:3)

IMPERIAL COLLEGE
(QS:6)

CORNELL UNIVERSITY (QS:16)

45/45 (IBDP)
GEORGIA INSTITUTE

43/45 (IBDP)
KELLY SCHOOL
The IB Biology SL Paper 1 Question Bank is a comprehensive resource for everything you need to know about the Paper 1 exam. It includes a wide range of questions, from easy to expert, so you can find the perfect level for your needs. The Question Bank also includes detailed answer explanations, so you can understand why each answer is correct. With this valuable resource at your disposal, you’ll be fully prepared to ace the Paper 1 exam!
Biology Standard Level Paper 1
Time: 45 minutes
Instructions to candidates
- Do not open this examination paper until instructed to do so.
- Answer all the questions.
- For each question, choose the answer you consider to be the best and indicate your choice on the answer sheet provided.
- The maximum mark for this examination paper is [30 marks].
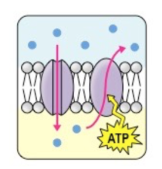
1.) The diagram is a model of one type of membrane protein function.
What is this type of membrane protein function?
A) Enzymatic activity
B) Active/Passive transport
C) Cell-to-cell recognition
D) Anchorage/Attachment
Solution: B
Explanation: Membrane proteins can serve a variety of key functions. The function outlined in the diagram is transport. Transport is responsible for facilitated diffusion and active transport.
2.) There are four main types of stem cells present at various stages of human development, which type describes multipotent cells?
A) Multipotent cells form any cell type, as well as extra-embryonic (placental) tissue (e.g. zygote)
B) Multipotent cells form any cell type (e.g. embryonic stem cells)
C) Multipotent cells can differentiate into a number of closely related cell types (e.g. haematopoietic adult stem cells)
D) Multipotent cells can not differentiate but are capable of self-renewal (e.g. progenitor cells, muscle stem cells)
Solution: C
Explanation: Multipotent cells can differentiate into a number of closely related cell types (e.g. haematopoietic adult stem cells)
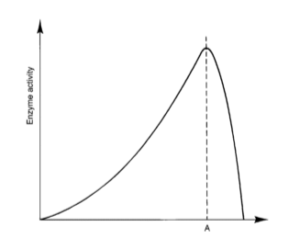
3.) What effect on enzymatic activity is shown on the x-axis of this image?
A) The Effect of Temperature on Enzyme Activity
B) The Effect of pH on Enzyme Activity
C) The Effect of Substrate Concentration on Enzyme Activity
D) The Effect of Salinity on Enzyme Activity
Solution: A
Explanation: Low temperatures result in insufficient thermal energy for the activation of an enzyme-catalysed reaction to proceeD) Increasing the temperature will increase the speed and motion of both enzyme and substrate, resulting in higher enzyme activity. High temperatures cause denaturation.
4.) In decreasing order, which greenhouse gases have the largest warming effect within the atmosphere?
A) Water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrogen oxides
B) Carbon dioxide, methane, nitrogen oxides, water vapour
C) Methane, carbon dioxide, water vapour, nitrogen oxides
D) Nitrogen oxides, methane, carbon dioxide, water vapour
Solution: A
Explanation: The greenhouse gases which have the largest warming effect within the atmosphere are water vapour (clouds) and carbon dioxide.
5.) Which animal phyla is matched to the correct description?
Solution: C) Cnidaria
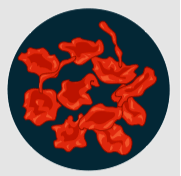
6.) The image shows a red blood cell that has been placed in a solution.
What type of solution is surrounding the red blood cell?
A) Hypertonic
B) Isotonic
C) Hypotonic
D) Osmotic
Solution: A
Explanation: In hypertonic solutions, water will leave the cell causing it to shrivel (crenation).
7.) What type of bond holds the complementary base pairs together in a double helix of DNA?
A) covalent bonds
B) peptide bonds
C) glycosidic bonds
D) hydrogen bonds
Solution: D
Explanation: The two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between pairs of bases: adenine pairs with thymine, and cytosine pairs with guanine.
8.) Which of the following is responsible for the red colour in blood?
A) Myoglobin
B) Hemocyanin
C) Haemoglobin
D) Platelets
Solution: C
Explanation: Haemoglobin is the protein found in the red blood cells, it primarily functions in the transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide. It renders red colour to the blood.
9.) What is the lifespan of RBCs?
A) 60 days
B) 100 days
C) 120 days
D) 40 days
Solution: C
Explanation: The maximum lifespan of RBCs is 120 days.
10.) What is the function of the cell membrane in a prokaryotic cell?
A) To protect the cell from external forces
B) To regulate the movement of substances into and out of the cell
C) To control the cell’s metabolic processes
D) To store genetic information
Solution: B
Explanation: The cell membrane in prokaryotic cells serves to regulate the movement of substances in and out of the cell. It is selectively permeable and allows for the transport of nutrients and waste products.
11.) Which of the following processes results in the formation of two genetically identical daughter cells?
A) Meiosis
B) Mitosis
C) Binary fission
D) Crossing over
Solution: B
Explanation: Mitosis is a process of cell division that results in the formation of two genetically identical daughter cells. It is an important process for growth and repair of tissues in multicellular organisms.
12.) What is the role of the Golgi apparatus in the cell?
A) To produce ATP
B) To synthesize proteins
C) To transport and modify proteins and lipids
D) To digest cellular waste
Solution: C
Explanation: The Golgi apparatus plays a key role in the sorting, modification, and transport of proteins and lipids within the cell. It is responsible for the packaging and delivery of these molecules to their final destinations.
13.) What is the role of the hypothalamus in the endocrine system?
A) To produce and release hormones that regulate metabolism
B) To secrete digestive enzymes in response to food intake
C) To regulate body temperature and fluid balance
D) To produce and release hormones that regulate other endocrine glands
Solution: D
Explanation: The hypothalamus is a small region of the brain that plays a key role in regulating the endocrine system. It produces and releases hormones that stimulate or inhibit the release of hormones from other endocrine glands throughout the body.
14.) A group of researchers are studying the effect of temperature on the growth rate of a particular species of bacteriA) They grow the bacteria in four different temperatures: 10°C, 20°C, 30°C, and 40°C They measure the growth rate of the bacteria in each temperature condition over a period of 24 hours. Based on the data presented in the case study, which of the following statements is most likely true?
A) The growth rate of the bacteria will be the same at all four temperatures.
B) The growth rate of the bacteria will be highest at 30°C.
C) The growth rate of the bacteria will be lowest at 10°C.
D) The growth rate of the bacteria will be highest at 40°C.
Solution: B
Explanation: Based on the data presented, the growth rate of the bacteria is highest at 30°C.
15.) Which of the following statements best explains the mechanism by which a nerve impulse is transmitted across a synapse?
A) The neurotransmitter molecules are released from the postsynaptic neuron, diffuse across the synaptic cleft, and bind to the receptors on the presynaptic neuron, causing depolarization.
B) The neurotransmitter molecules are released from the presynaptic neuron, diffuse across the synaptic cleft, and bind to the receptors on the postsynaptic neuron, causing depolarization.
C) The action potential travels along the postsynaptic neuron and activates voltage-gated calcium channels, which release neurotransmitter molecules into the synaptic cleft, causing depolarization.
D) The action potential travels along the presynaptic neuron and activates voltage-gated sodium channels, which release neurotransmitter molecules into the synaptic cleft, causing depolarization.
Solution: B
Explanation: The neurotransmitter molecules are released from the presynaptic neuron, diffuse across the synaptic cleft, and bind to the receptors on the postsynaptic neuron, causing depolarization.
16.) The protein channels in the plasma membrane of a cell are responsible for which of the following processes?
A) Active transport
B) Passive transport
C) Both active and passive transport
D) Facilitated diffusion only
Solution: C
Explanation: Protein channels in the plasma membrane can facilitate both active and passive transport, depending on the concentration gradients and the energy requirements of the substances being transported.
17.) A population of deer is introduced to a new area where the vegetation is primarily coniferous trees. After several generations, the deer population is found to have a higher frequency of individuals with thicker coats of fur. Which of the following mechanisms of evolution is most likely responsible for this change?
A) Genetic drift
B) Natural selection
C) Gene flow
D) Mutation
Solution: B
Explanation: In this case, the thicker fur coats provide an advantage to the deer in the colder climate of the new area, and those individuals are more likely to survive and reproduce, passing on their advantageous traits to their offspring. This is an example of natural selection.
18.) A researcher is studying a population of birds that feed on insects found in tree bark. The researcher notes that birds with longer beaks are more successful at feeding on insects in deeper crevices in the bark. Over time, the average beak length in the population increases. Which of the following processes is responsible for this change?
A) Genetic drift
B) Natural selection
C) Gene flow
D) Mutation
Solution: B
Explanation: In this case, the longer beaks provide an advantage to the birds in accessing their food source, and those individuals are more likely to survive and reproduce, passing on their advantageous traits to their offspring. This is an example of natural selection.
19.) A student is studying the genetic basis of a rare genetic disease in a family. The disease is caused by a mutation in a single gene. Which of the following patterns of inheritance is most likely responsible for the transmission of the disease in this family?
A) Autosomal dominant
B) Autosomal recessive
C) X-linked dominant
D) X-linked recessive
Solution: B
Explanation: If the disease is caused by a mutation in a single gene, and individuals with only one copy of the mutated gene do not exhibit the disease, then it is most likely inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern, where individuals must inherit two copies of the mutated gene to exhibit the disease.
20.) A group of researchers is studying the effects of a new drug on cancer cells. They find that the drug inhibits the activity of an enzyme that is critical for cell division. Which of the following phases of the cell cycle is most likely affected by the drug?
A) G1
B) S
C) G2
D) M
Solution: D
Explanation: The M phase of the cell cycle is when cell division occurs, and the drug is inhibiting an enzyme critical for this process.
21.) A population of fish is introduced to a new lake where there are no predators. Over time, the population of fish increases rapidly, but the average size of the fish decreases. Which of the following mechanisms of evolution is most likely responsible for this change?
A) Genetic drift
B) Natural selection
C) Gene flow
D) Mutation
Solution: A
Explanation: In this case, the absence of predators removes a selective pressure for larger fish, and the population experiences genetic drift, with smaller fish being more likely to survive and reproduce due to chance.
22.) A group of researchers is studying the genetic basis of a rare disease that affects only males. They find that the disease is caused by a mutation on the X chromosome. Which of the following patterns of inheritance is most likely responsible for the transmission of the disease in this family?
A) Autosomal dominant
B) Autosomal recessive
C) X-linked dominant
D) X-linked recessive
Solution: D
Explanation: If the disease is caused by a mutation on the X chromosome and affects only males, it is most likely inherited in an X-linked recessive pattern, where males only inherit one X chromosome and are more likely to exhibit the disease if they inherit the mutated gene.
23.) A group of researchers is studying the role of different hormones in the regulation of blood glucose levels. They find that the hormone insulin decreases blood glucose levels, while the hormone glucagon increases blood glucose levels. Which of the following glands is responsible for secreting these hormones?
A) Pituitary gland
B) Thyroid gland
C) Adrenal gland
D) Pancreas
Solution: D
Explanation: The pancreas is responsible for secreting insulin and glucagon, which play critical roles in the regulation of blood glucose levels.
24.) A population of rabbits is introduced to a new island with limited resources. Over time, the average body size of the rabbits decreases, and the population experiences a decrease in genetic diversity. Which of the following mechanisms of evolution is most likely responsible for this change?
A) Genetic drift
B) Natural selection
C) Gene flow
D) Mutation
Solution: A
Explanation: In this case, the limited resources of the new island create a selective pressure for smaller body size, and the population experiences genetic drift due to chance events, with smaller rabbits being more likely to survive and reproduce.
25.) A group of researchers is studying the differences in gene expression between cancer cells and healthy cells. They find that several genes are upregulated in the cancer cells, leading to increased cell division and growth. Which of the following cellular processes is most likely affected by the upregulated genes?
A) DNA replication
B) Transcription
C) Translation
D) Protein folding
Solution: B
Explanation: Transcription is the process by which DNA is converted into RNA, which can then be translated into proteins. Upregulated genes in cancer cells would result in increased transcription of these genes, leading to increased protein production and cell growth.
26.) A researcher is studying the effects of a new pesticide on a population of insects. After several generations, the population becomes resistant to the pesticide. Which of the following mechanisms of evolution is most likely responsible for this change?
A) Genetic drift
B) Natural selection
C) Gene flow
D) Mutation
Solution: B
Explanation: In this case, the exposure to the pesticide creates a selective pressure for insects that are resistant to the pesticide, and those individuals are more likely to survive and reproduce, passing on their resistant traits to their offspring. This is an example of natural selection.
27.) Which of the following structures is not found in prokaryotic cells?
A) Ribosomes
B) Cell wall
C) Nucleus
D) Plasma membrane
Solution: C
Explanation: Prokaryotic cells lack a distinct nucleus, and their genetic material is not separated from the cytoplasm by a nuclear membrane.
28.) A researcher is studying the effects of temperature on the rate of enzyme-catalyzed reactions. Which of the following graphs best represents the relationship between temperature and enzyme activity?
A) A linear graph with a positive slope
B) A linear graph with a negative slope
C) A curved graph with a maximum point
D) A curved graph with a minimum point
Solution: C
Explanation: Enzymes have an optimal temperature at which they function most efficiently, and activity decreases as the temperature deviates from this optimum in either direction. Therefore, the graph would show a curved relationship with a maximum point.
29.) What is the name of the organelle that is responsible for the synthesis of lipids?
A) Mitochondria
B) Ribosome
C) Lysosome
D) Endoplasmic reticulum
Solution: D
Explanation: The endoplasmic reticulum is an organelle responsible for lipid synthesis.
30.) In what phase of mitosis do chromosomes align at the equator of the cell?
A) Prophase
B) Metaphase
C) Anaphase
D) Telophase
Solution: B
Explanation: During metaphase, chromosomes align at the equator of the cell.