costs and revenues Notes
Costs
Cost of production refers to the total amount spent by an organization in the process of production of output. The cost includes both the cost of setting up the business as well as the cost of running the operations.
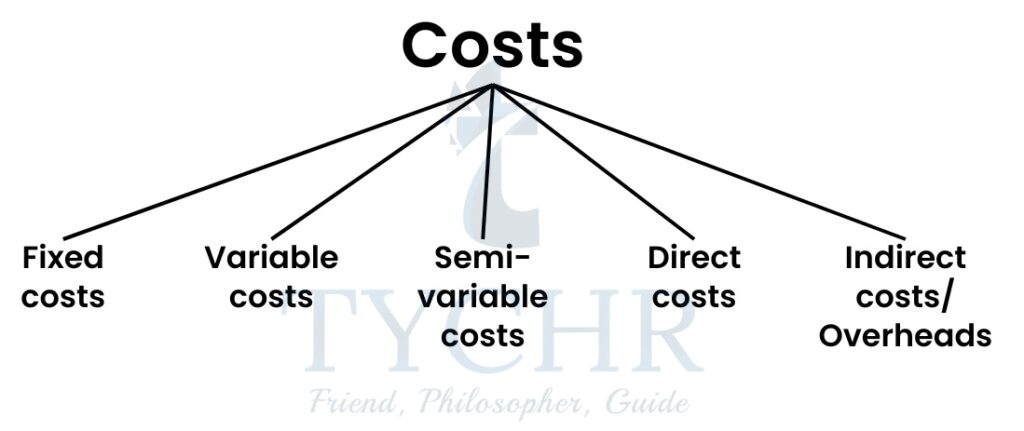
FIXED COSTS:
- Cost of production that must be paid by the business organization even if there is no production.
- Few examples of fixed costs are interest payments on rent/ lease payments, etc.
- Fixed costs can change but this change is independent of the level of output.
- Examples of fixed cost: Rent of land, Lease payments, salaries of workers, etc.
VARIABLE COSTS:
- Variable costs are the costs that change in proportion with the change in output.
- Theoretically, if the production is zero, then VC = 0.
- Variable costs and the output level are positively correlated. Increase in output level = increase in VC, decrease in output level = decrease in VC.
- Example: Purchase of raw materials
The graph below shows the relation between level of output and the costs.
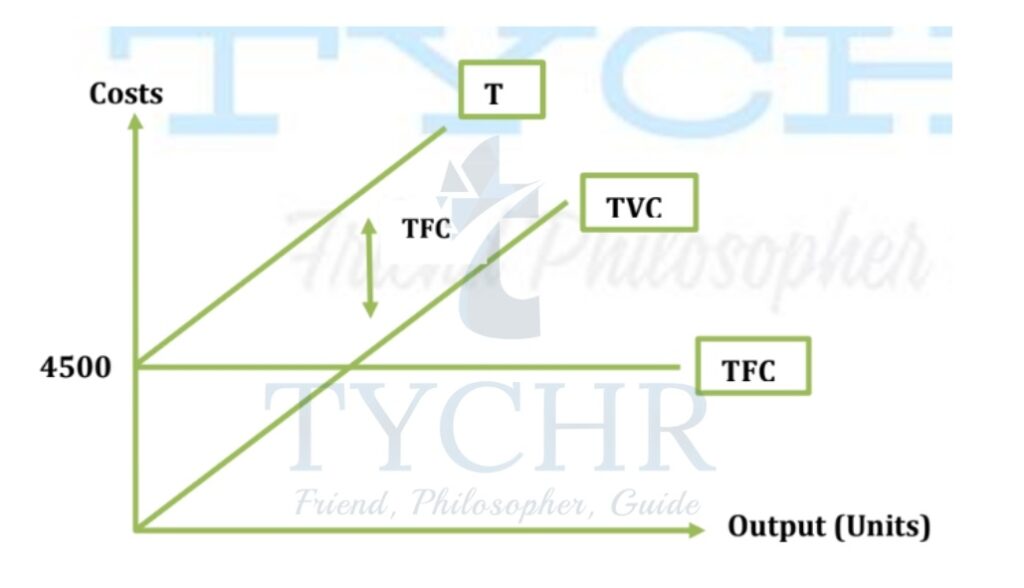
TC (Total cost of production) = TFC (Total fixed cost) + TVC (Total variable cost)
SEMI- VARIABLE COSTS:
- Semi- variable costs are the combination of fixed and variable costs.
- Till a certain level of output, the cost is fixed (the cost does not change with the change in level of output), but after that, the cost starts changing in proportion with the level of output.
- Example: Electricity bill. The bill may be fixed till a certain limit of usage. But once the quota/ limit exceeds, the bill may become variable.
DIRECT COSTS:
- Direct costs are the costs that are directly related to the production of output (good or service).
- The costs which can be wholly traced which can either be a service, a product or department.
- Direct costs can include both fixed costs and variable costs.
- Example: Direct material, direct labor, etc.
INDIRECT COSTS:
- Indirect costs are also known as overheads.
- The costs that cannot be traced to the production of any single output.
- For example: Electricity and lighting expenses, legal expenses, etc. cannot be identified with any single product.
IMPORTANT COST FORMULAE:
- TC = TFC + TVC
- TVC = AVC ×Q
- TFC = AFC ×Q
- AFC = TFC/Q
- AVC= TVC/Q
AVC = Average variable cost, AFC = Average fixed cost, Q= Level of output
TOTAL COST AND AVERAGE COST:
Total cost – Total cost refers to the aggregate of all the fixed and variable costs associated with the production of output.
Marginal cost- Marginal cost, on the other hand, refers to the change in total cost when the level of output increases by one unit. (MC = 𝐓𝐂𝐐+𝟏 − 𝐓𝐂𝐐)
Revenue
Sales Revenue refers to the amount of money that acts as income for the business. The revenue is the money generated from the sale of goods and services to the customers.
Sales revenue = Price of the product × Quantity sold
For e.g.: If the price of each of the 10 units of chocolate produced is Rs. 50, then the total sales revenue for the business would be Rs.
500. Average revenue = 500/10 = Rs. 50
Other revenue includes the revenue items generated from other sources, not from the sale of goods/ services. Some of the sources for non- sales revenue are mentioned below:
- Advertising – Companies such as Google, YouTube, Facebook make a high percentage of their income from advertising. They receive the advertising money from advertisers only when customers click on the ads.
- Transaction fees – The financial institutions such as banks charge transaction fees from the customers and generate a portion of their revenue from these fees.
- Sponsorship revenue –Sponsorship is the financial support received by the sponsoring organization (sponsor) to promote the brand of donor.
- Franchise costs and royalties – Franchisor receives the fee from the franchisees to grant them the right to use the company’s brand name, logo, and trademark. For e.g.: Dominos, McDonalds, etc. all operate their franchisees.

- Subscription fees – Yearly/ monthly subscription and membership fees are charged by various organizations. For e.g.: Streaming websites such as Netflix, Hotstar, etc.
- Dividend – The companies which invest in the shares of other companies receive dividends as a shareholder.
- Interest earnings – The companies earn interest on their deposits at bank.
- Subventions – These are subsidies offered by the government to help the businesses provide the necessities to the marginal households at lower prices. The financial support acts as a compensation for these businesses.
- Donations – Charitable and non- profit organizations receive ample amounts of donations from various people dedicated to contribute for the social cause.
In this chapter, we discussed the meaning of cost and revenue, different categories of costs and their examples, sources of revenue. We also need to know that an organization needs to manage the costs effectively utilizing the resources to the optimum level, so that there is increased profitability. Cost control is crucial to maintain the overall profitability of the enterprise.
PROFIT = TR – TC, where TR = Total Sales
Revenue = P × Q and TC = TFC + TVC

